-By: Bhavisha Changrani
The Mediterranean Diet has become synonymous with longevity, good health, and a way of life that promotes both physical well-being and an overall sense of vitality. Based on the traditional eating patterns of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea — such as Italy, Greece, Spain, and southern France — this diet emphasizes the consumption of nutrient-dense, whole foods, balanced in a way that supports optimal health. More than just a diet, it’s a lifestyle that fosters sustainable, healthy eating habits while contributing to overall wellness.
In recent years, scientific research has highlighted the numerous health benefits associated with the Mediterranean Diet. From heart health and weight management to reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, stroke, and certain cancers, this diet stands out for its well-rounded approach to nutrition. It emphasizes an abundance of fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and healthy fats, particularly olive oil, while encouraging moderate consumption of fish, poultry, dairy, and red wine.
This article will explore the health benefits of the Mediterranean Diet, delve into the science behind its effectiveness, and provide practical tips on how to adopt this diet, particularly for beginners. Whether you’re looking to reduce the risk of chronic diseases, improve your heart health, or simply enjoy a more sustainable way of eating, the Mediterranean Diet can serve as a pathway to achieving those goals.

Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet
Heart Health
The Mediterranean diet’s beneficial effects on cardiovascular health are among its best-known advantages. Heart-healthy fats, especially unsaturated fats from nuts and olive oil, are abundant in the Mediterranean diet and help reduce LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, also known as “bad cholesterol.” Consequently, this lowers the chance of heart disease and stroke.Research has consistently shown that people who follow a Mediterranean-style eating plan have a lower incidence of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular problems. For instance, the PREDIMED study, one of the largest trials on the Mediterranean Diet, found that individuals who adhered to the diet had a 30% lower risk of cardiovascular events compared to those following a low-fat diet.
Moreover, the diet’s emphasis on antioxidant-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and herbs, further contributes to heart health by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which play a role in the development of heart disease.
Weight Management
In addition to its heart-healthy benefits, the Mediterranean Diet has also been shown to help with weight management. Unlike restrictive fad diets, the Mediterranean Diet promotes a balanced approach to eating that includes nutrient-dense foods while avoiding overly processed, high-calorie options.
Studies suggest that people following the Mediterranean Diet tend to maintain a healthy weight or lose weight gradually, as it emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods that are naturally filling and nutrient-rich. The healthy fats found in olive oil and nuts, along with fiber-rich vegetables, fruits, and legumes, help keep hunger at bay while promoting a feeling of fullness, reducing the likelihood of overeating.
A 2016 study published in the New England Journal of Medicine showed that those who followed a Mediterranean Diet had greater success in weight loss compared to those following a low-fat diet. This is likely due to the high nutrient density of the foods consumed, which enables the body to function optimally without the need for excessive caloric intake.
Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases

The Mediterranean Diet has been extensively studied for its potential to reduce the risk of various chronic diseases, including diabetes, hypertension, and certain cancers.
Type 2 Diabetes
The Mediterranean Diet’s focus on whole grains, legumes, and healthy fats may help improve insulin sensitivity, making it easier for the body to regulate blood sugar levels. Research has shown that individuals who follow a Mediterranean-style diet have a significantly lower risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. A systematic review published in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology concluded that the diet was associated with a 24% reduced risk of Type 2 diabetes.
Cancer
Diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants have been shown to reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, such as breast, colorectal, and prostate cancer. The Mediterranean Diet provides a wealth of polyphenols and other compounds that have been shown to inhibit cancer cell growth and reduce inflammation, both of which contribute to cancer prevention.
Alzheimer’s and Cognitive Decline
One of the more intriguing benefits of the Mediterranean Diet is its potential to reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of cognitive decline. A study published in Archives of Neurology showed that individuals who followed the Mediterranean Diet had a 40% lower risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. The diet’s rich antioxidant content and anti-inflammatory properties are believed to contribute to this effect, preserving brain health and cognitive function as people age.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Chronic inflammation is a significant factor in the development of various diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. The Mediterranean Diet is rich in anti-inflammatory foods such as fatty fish (rich in omega-3 fatty acids), olive oil (high in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants), and vegetables (packed with fiber and phytonutrients). These foods help reduce levels of inflammation in the body, which plays a pivotal role in protecting against chronic diseases.
A 2015 study in the Journal of Nutrition found that the Mediterranean Diet significantly decreased biomarkers of inflammation, further supporting the idea that this eating pattern can contribute to long-term health.
Longevity
People in Mediterranean regions tend to live longer, healthier lives. The combination of a nutrient-dense diet, a healthy relationship with food, and an active lifestyle (including physical activity and socializing) has been linked to increased life expectancy.
A study published in The BMJ in 2013 found that adherence to the Mediterranean Diet was associated with a lower risk of mortality and a longer life. This diet’s ability to prevent chronic diseases and improve overall health likely plays a key role in its connection to longevity.

How to Adopt the Mediterranean Diet for Beginners
Adopting the Mediterranean Diet doesn’t require a complete overhaul of your eating habits. It’s about making gradual changes and choosing whole, natural foods that nourish the body. For beginners, here are some practical tips to help you integrate the Mediterranean Diet into your lifestyle:
Focus on Whole, Unprocessed Foods
The foundation of the Mediterranean Diet is fresh, whole foods. Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains (such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat), legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas), and nuts (almonds, walnuts, pistachios) into your meals. Essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants that promote general health are found in these foods.
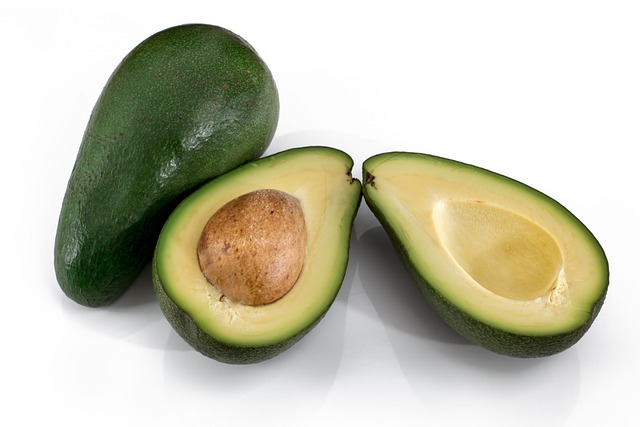

Prioritize Healthy Fats
One of the key components of the Mediterranean Diet is the inclusion of healthy fats, particularly from olive oil. Replace unhealthy fats, such as trans fats or processed oils, with extra virgin olive oil for cooking and dressings. Monounsaturated fats, which are abundant in olive oil, are good for the heart.Additionally, nuts and seeds (such as chia, flaxseeds, and almonds) are excellent sources of healthy fats and can be added to salads, smoothies, and snacks.
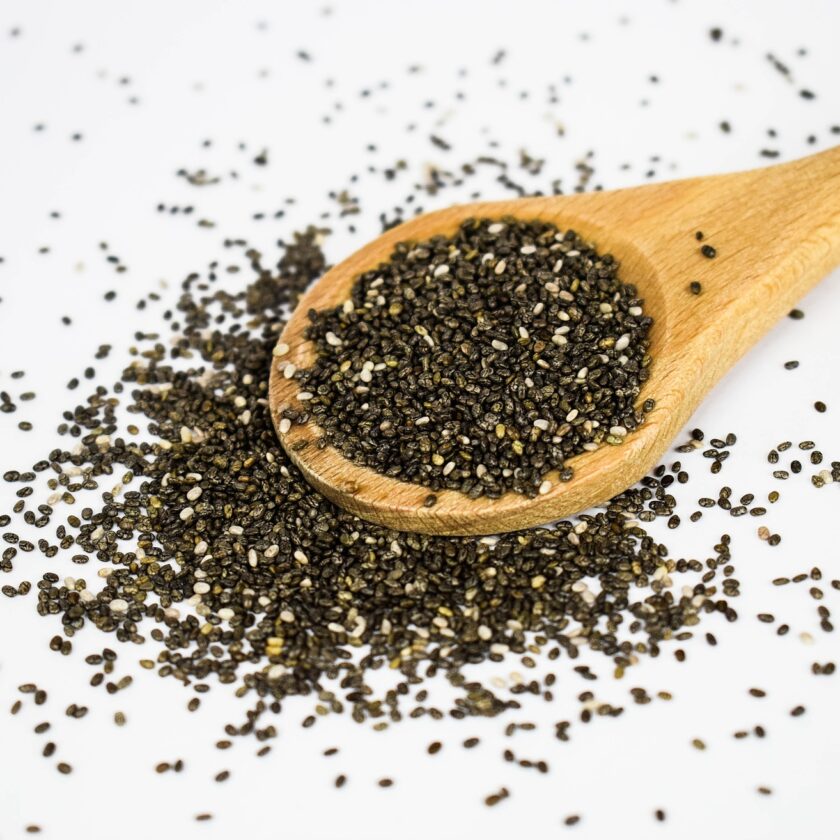

Eat More Fish and Seafood
The Mediterranean Diet encourages the consumption of fish and seafood, particularly oily fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, and anchovies. These fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for heart health and reducing inflammation.
Limit Red Meat and Dairy
While the Mediterranean Diet doesn’t completely eliminate meat, it encourages moderate consumption of red meat and dairy products. Focus on lean meats like chicken and turkey, and try to incorporate plant-based protein sources such as legumes, tofu, and tempeh. Dairy is consumed in moderation, often in the form of cheese or yogurt. Opt for lower-fat or fermented options to enhance digestive health.
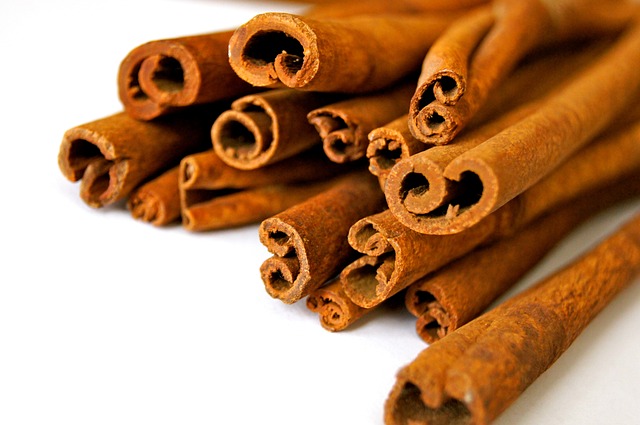

Embrace Herbs and Spices
Instead of relying on salt, the Mediterranean Diet encourages the use of herbs and spices to flavor food. Common Mediterranean herbs include basil, oregano, thyme, rosemary, garlic, and cinnamon. These herbs not only add flavor but also offer health benefits, as many of them have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and digestive properties.
Enjoy Red Wine in Moderation
Red wine is a staple of the Mediterranean Diet, but it’s important to consume it in moderation. Studies have shown that moderate wine consumption (about one glass per day) is associated with improved heart health and reduced risk of chronic diseases. However, it’s essential to drink responsibly and consult with your healthcare provider, especially if you have any health conditions.
Create Balanced Meals
A typical Mediterranean meal includes a variety of components: a generous serving of vegetables, a portion of whole grains, a protein source (fish, poultry, legumes), and a drizzle of olive oil. Aim to balance your meals by including a variety of food groups to ensure you’re getting a broad range of nutrients.
Make it a Lifestyle, Not a Fad
The Mediterranean Diet is about adopting a long-term, sustainable lifestyle, rather than a short-term, restrictive diet. It encourages mindful eating, enjoying meals with family and friends, and staying active. Walking, cycling, and swimming are examples of physical activities that are essential to the Mediterranean way of life.

Conclusion
The Mediterranean Diet is much more than a way of eating; it’s a comprehensive lifestyle that promotes health, longevity, and well-being. Rich in heart-healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants, this diet can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases, improve weight management, and enhance overall quality of life. By focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods, embracing healthy fats, and limiting processed foods, you can reap the benefits of this time-honored eating pattern. Whether you’re looking to improve heart health, manage weight, or simply enjoy a more balanced and sustainable way of eating, the Mediterranean Diet offers an accessible and delicious path to better health.