-By: Bhavisha Changrani
Depression, a pervasive mental health condition affecting millions worldwide, is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, loss of interest or pleasure in activities, and disruptions in sleep and appetite. While traditional treatments like therapy and medication are essential, emerging research suggests that dietary choices play a significant role in managing depression. This article explores the connection between diet and depression and offers insights into how making informed dietary changes can positively impact mental health.

The Gut-Brain Connection
The gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication network between the gastrointestinal tract and the central nervous system, plays a crucial role in regulating mood, cognition, and emotional well-being. Emerging evidence suggests that the composition of gut microbiota, influenced by dietary factors, can influence neurotransmitter production, inflammation levels, and stress response systems, all of which are implicated in depression.
Key Nutrients for Mental Health
Several nutrients have been linked to improved mood and reduced risk of depression. These include:
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Found abundantly in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, omega-3 fatty acids are essential for brain health and have been associated with lower rates of depression. They exert anti-inflammatory effects and support neurotransmitter function, promoting mood stability and resilience.
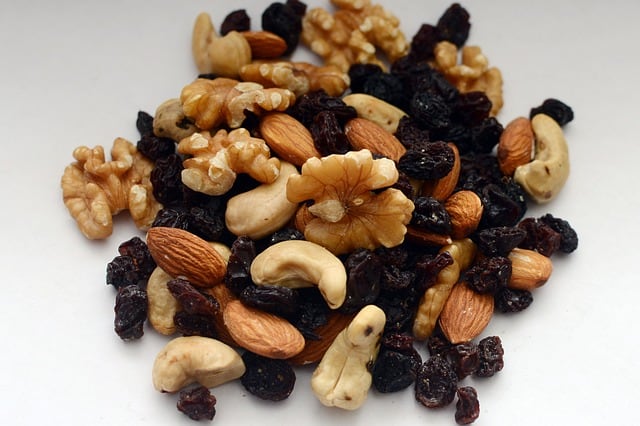

B Vitamins
B vitamins, including folate, B6, and B12, play critical roles in neurotransmitter synthesis and methylation processes implicated in depression. Foods rich in B vitamins such as leafy greens, legumes, whole grains, and lean meats should be included in a depression-fighting diet.
Antioxidants
Antioxidant-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, help combat oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which contribute to depression. Vitamins C and E, as well as phytonutrients like flavonoids and carotenoids, possess potent antioxidant properties that support brain health and mood regulation
Probiotics
Probiotics, beneficial bacteria found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, can modulate gut microbiota composition and promote a healthy gut-brain axis. Studies suggest that probiotic supplementation may alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety by reducing inflammation and enhancing neurotransmitter function.
Tryptophan-Rich Foods
Tryptophan, an amino acid precursor to serotonin, a neurotransmitter involved in mood regulation, can be obtained from protein-rich foods such as poultry, eggs, dairy, tofu, and legumes. Consuming tryptophan-rich foods may support serotonin production and improve mood.

Dietary Strategies for Depression Management
Incorporating the following dietary strategies into your daily routine can support mental health and aid in the management of depression:Prioritize Whole Foods: Emphasize whole, minimally processed foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your diet. These nutrient-dense foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients that support overall health and mood.
Increase Omega-3 Intake
Consume fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines regularly or consider supplementing with high-quality fish oil to boost omega-3 fatty acid levels and support brain health.

Include Probiotic Foods
Incorporate fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, kombucha, and tempeh into your diet to promote a healthy gut microbiome and optimize gut-brain communication.
Limit Sugar and Processed Foods
Minimize intake of refined sugars, processed snacks, and high-fat, high-sugar foods, which can contribute to inflammation, dysbiosis, and mood fluctuations.
Stay Hydrated
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated, support cognitive function, and maintain overall well-being.
Conclusion
While diet alone cannot cure depression, adopting a nutrient-rich diet and making informed dietary choices can complement traditional treatments and support mental health and well-being. By nourishing the body and mind with wholesome foods rich in essential nutrients, individuals can optimize brain function, balance mood, and enhance resilience against depression. As research in nutritional psychiatry continues to evolve, integrating dietary interventions into comprehensive treatment plans holds promise for improving outcomes and empowering individuals on their journey towards mental health recovery.